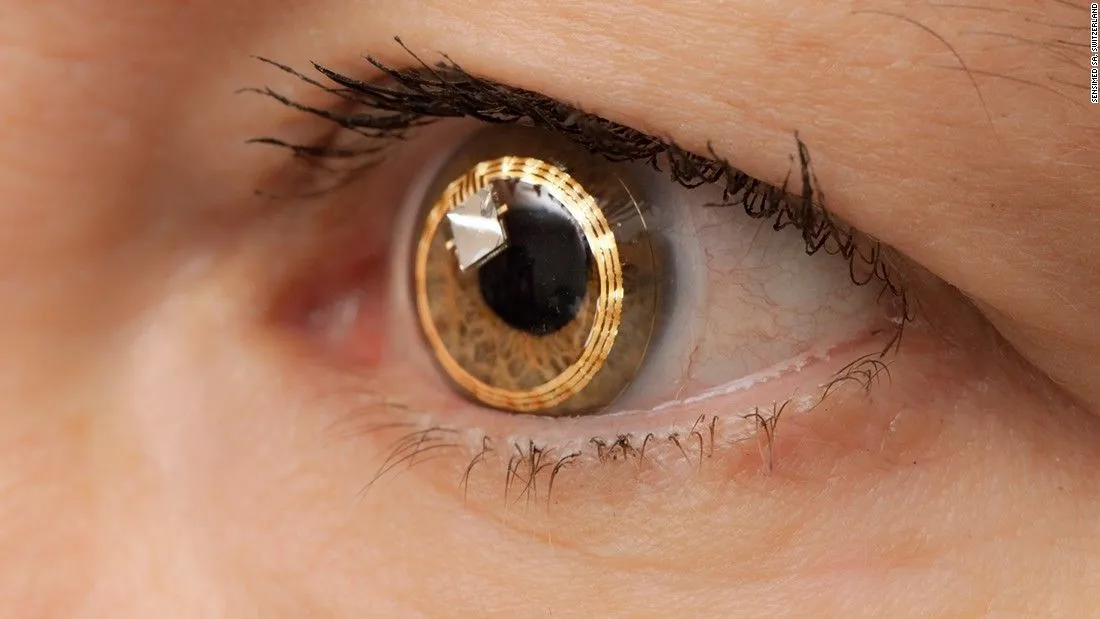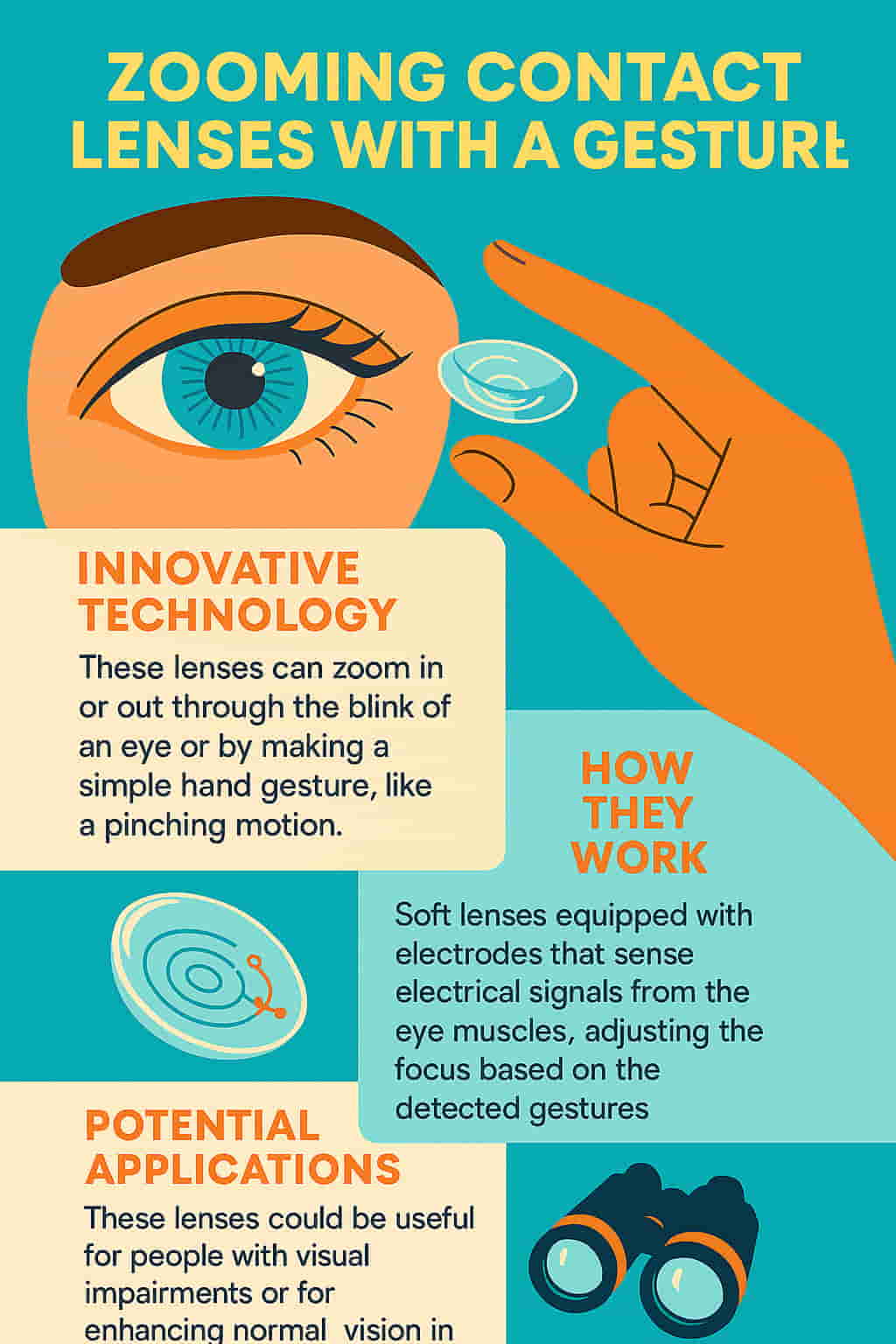
Imagine adjusting your vision with just the blink of an eye. What once sounded like sci-fi is now edging closer to reality. Scientists have developed smart contact lenses that zoom, responding to simple eye movements. These revolutionary lenses may soon transform how we see the world—literally.
This article explores the technology behind zoomable smart lenses, their future applications, and how they could reshape everything from eye care to augmented reality.
What Are Smart Contact Lenses That Zoom?
The term “smart contact lenses that zoom” refers to high-tech optical lenses embedded with sensors and responsive materials that allow users to control focal length and zoom with natural eye movements—like blinking or looking in a specific direction.
These aren’t your average vision-correcting lenses. Instead, they act like miniature computers inside the eye, powered by biometric signals. When you blink twice or move your eye in a set direction, they trigger a change in magnification or adjust focus in real-time.
Early prototypes have been developed by scientists at institutions such as the University of California, San Diego, where researchers have created soft robotic lenses that respond to electro-oculographic signals—tiny electrical impulses generated by eye movement (source: UCSD News).
How Smart Contact Lenses That Zoom Actually Work
The magic behind smart contact lenses that zoom lies in their materials and embedded electronics. These lenses contain:
-
Electro-responsive polymers: Flexible materials that change shape when exposed to electrical signals.
-
Eye-movement sensors: Electrodes detect muscle activity around the eye to interpret commands.
-
Microcontrollers: Tiny circuits process the data and direct the lens to zoom or focus accordingly.
When you blink twice or look to the side, the sensors detect the movement and send a command to reshape the lens. This reshaping changes the focal point, effectively allowing zooming or auto-focus.
To learn more about this technology, check out this report from IEEE Spectrum, a trusted source for cutting-edge engineering innovations.
Applications of Smart Contact Lenses That Zoom
This technology isn’t just about convenience—it could revolutionize multiple industries:
1. Enhanced Vision for the Visually Impaired
Individuals with low vision could benefit from lenses that adjust zoom and focus on demand. It could help them read signs, recognize faces, or navigate unfamiliar environments more easily.
2. Hands-Free Augmented Reality (AR)
Imagine integrating zoomable lenses with real-time digital overlays. Instead of bulky headsets, smart contact lenses that zoom could allow AR displays directly within your natural vision. Companies like Mojo Vision are already exploring this space.
3. Military and Tactical Use
Soldiers could zoom in on distant targets or survey terrain without binoculars or riflescopes. Real-time zooming could be a tactical advantage in surveillance or combat scenarios.
4. Consumer Photography
Zooming lenses could be paired with wearable cameras, enabling photographers and vloggers to focus with their eyes alone.
Advantages Over Traditional Visual Tech
-
Discreet: Unlike glasses or headsets, smart lenses are practically invisible.
-
Natural interface: Controlled entirely by eye movement—no hands, no buttons.
-
Futuristic integration: Could pair with smartphones, AR glasses, or even health-monitoring devices.
Explore innovations in wearable tech at The Verge’s technology section to follow updates on future products.
Smart Contact Lenses That Zoom – The Challenges Ahead
While promising, there are hurdles to overcome:
⚠️ Safety and Health
Any device inserted into the eye must be rigorously tested for biocompatibility. Irritation, long-term wear effects, and optical safety are all under review.
⚠️ Power Supply
Current designs require external battery packs or wireless charging—a major obstacle for everyday use. Future versions will need micro-scale energy solutions.
⚠️ Data Security
Since smart lenses may collect data (eye tracking, gaze location), privacy and cybersecurity become crucial concerns. Users must trust that their vision isn’t being tracked for the wrong reasons.
Current Research and Prototypes
Several institutions and startups are pushing the envelope in smart lens development:
-
UC San Diego: Soft robotic lens controlled by electro-oculographic signals. Early-stage prototype with 2x zoom on command.
-
Mojo Vision: Smart lenses with built-in displays. Their goal: seamless AR with eye-based zoom and navigation (Mojo Vision).
-
Samsung and Sony have filed patents for camera-integrated contact lenses, potentially enabling future zoom functionality.
These breakthroughs are still in prototype or pre-commercial stages, but clinical trials and investor interest are growing rapidly.
Outbound Resources for Further Reading
-
Harvard Wyss Institute: Bio-integrated soft electronics
-
National Eye Institute (NEI): Vision research and innovation updates
-
MIT Technology Review: Smart lens innovation and ethical implications
FAQs
Q1: What are smart contact lenses that zoom?
They are next-generation contact lenses that use sensors and soft electronics to allow the user to zoom or adjust focus using eye movements.
Q2: Are they available for consumers?
Not yet. Most versions are still in lab or prototype stages and not available for commercial sale.
Q3: How do they get power?
Current prototypes use external batteries or wireless power. Future versions aim to integrate ultra-small internal batteries or bio-harvesting methods.
Q4: Could they replace smartphones or glasses?
Possibly, especially when combined with AR tech. But that’s still years away.
Q5: Are they safe?
Safety testing is ongoing. Ensuring the lenses don’t irritate the eyes or cause long-term harm is a top priority for developers.