What happens when music meets robotics? In a small Greek lab, engineers recently introduced a groundbreaking performer—not a dancer in the traditional sense, but a robot designed to move with musical rhythm. Unlike industrial machines that perform repetitive tasks, this robot listens, adapts, and grooves to the beat. It’s a vibrant showcase of what’s now known as dancing robot technology, a field that fuses artificial intelligence with the expressive power of movement.
This might sound like a novelty, but it marks a new era of interaction—where technology becomes part of cultural expression, not just a silent background force.
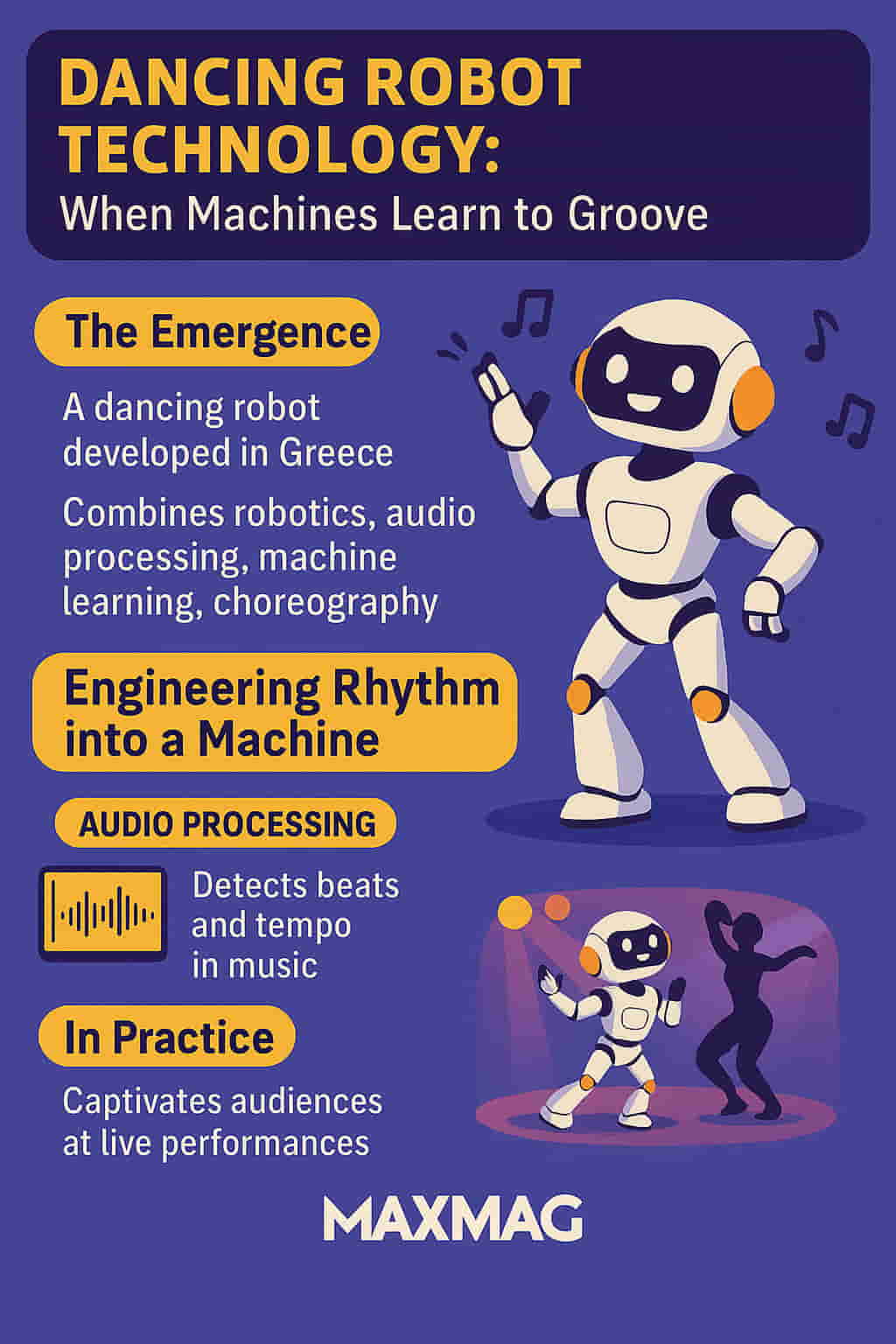
The Emergence of Dancing Robot Technology
At the heart of dancing robot technology is a blend of disciplines: robotics, audio signal processing, choreography, and machine learning. The Greek-built robot—nicknamed “Ari”—is one of the most recent examples of this convergence. Ari isn’t programmed with fixed dance routines. Instead, it listens to music live and adjusts its moves in real time, a feat that’s only possible through advanced beat-detection algorithms and responsive motor systems.
Ari represents a growing push in robotics to move beyond utility into personality. In a similar spirit, researchers at the MIT Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab (CSAIL) have been developing systems that let robots interpret dance moves through machine learning—bridging technical precision with fluid performance.
Engineering Rhythm into a Machine
To make a robot dance in real time, you need more than a clever script. Ari’s creators developed a full suite of tools for musical analysis, balance control, and expressive motion. First, the robot captures sound via an onboard microphone. Using algorithms similar to fast Fourier transforms, it identifies musical tempo, beats, and structural cues like choruses or breakdowns.
From there, a motion-planning engine interprets that rhythm into gestures. If the beat is slow, Ari might sway gently. If the song picks up, Ari can pivot, wave, or tilt with increasing intensity—all while maintaining balance through its internal gyroscope and accelerometers.
This ability to “feel” and react to music is what truly defines dancing robot technology. As seen in early research by The Kennedy Center, integrating dance and robotics helps reveal how movement can communicate emotional tone—even through machines.
Dancing Robot Technology in Practice
Captivating Live Performances
Ari made its debut during a DJ-led tech night in Athens. The moment the bass dropped, so did the audience’s jaws. Ari swayed, dipped, and spun in perfect sync with the track. But what stood out most was its sense of timing—not mechanical, but intentional. It was, by all appearances, dancing.
Footage of the event spread rapidly on social media, not only for the spectacle but because it hinted at a future where robots don’t just serve or compute—but perform. This is the kind of innovation that captures imaginations across tech and the arts.
Beyond Entertainment: Real-World Impact
Although thrilling on stage, dancing robot technology holds promise far beyond performance. In therapeutic settings, rhythm can be a powerful tool. According to Cleveland Clinic, music-based therapy improves motor skills, mood, and emotional regulation—especially for people with neurological conditions like Parkinson’s or autism.
Now imagine a robot that can replicate those motions with precision and repeatability. It could become a vital tool in hospitals, rehab centers, and classrooms—teaching children to clap along to beats or helping stroke patients regain coordination.
How Dancing Robot Technology Actually Works
The complexity behind Ari’s choreography isn’t visible to the naked eye, but it’s built from layers of sophisticated systems. Here’s how dancing robot technology operates at a functional level:
-
Audio Processing: Analyzes live sound, breaking it into tempo (BPM), volume, and frequency ranges.
-
Motion Trigger Engine: Maps audio patterns to movement categories such as step-touch, body wave, or spin.
-
Motor Control Interface: Translates these movements into electrical signals sent to servo motors that move arms, hips, or torso.
-
Balance System: Uses gyroscopic feedback to maintain posture while the robot shifts or tilts.
-
Gesture Variation: Injects small changes into repeated motions—such as an angled head nod or offset timing—so the performance feels less robotic and more expressive.
These components make it possible for a machine to interpret music rather than just mimic choreography.
Artists + Engineers = Magic
One of the reasons Ari feels so alive is the team behind it. Engineers collaborated with choreographers from the beginning to develop a movement library that mimics human gestures. For example, they considered how different genres evoke different body language—graceful flowing movements for ambient tracks, sharp angular ones for techno.
They also partnered with musicians who tested Ari’s response to shifting tempos and dynamic beats. This hands-on feedback helped the engineers fine-tune the algorithms and make Ari feel more like a performer than a machine.
This kind of partnership mirrors projects like those at MIT Media Lab’s Social Robots group, where expressive robotics aims to foster empathy and connection between humans and machines.
A Cultural Moment
When Ari performed traditional Greek folk dances during a national tech exhibition, it stirred something powerful: a robot honoring heritage. In a space often dominated by Western pop or techno, seeing a robot dance to bouzouki music reminded audiences that dancing robot technology isn’t culturally monolithic—it’s adaptable, inclusive, and global.
This cultural resonance deepens the meaning behind Ari’s existence. The robot isn’t just performing—it’s participating in tradition. And that changes how people relate to it.
The Future of Robotic Dancing
The roadmap for dancing robot technology is full of exciting possibilities:
-
Dance Companions: Robots that learn your moves and join you on the dance floor using visual tracking and AI prediction.
-
Custom Dance Uploads: Imagine uploading a choreography file to your home robot and watching it perform a trending TikTok routine.
-
Group Performances: Multiple robots dancing together, coordinated by Wi-Fi timing protocols or even choreographed alongside human dancers.
-
Educational Play: Teaching children about rhythm, sequencing, and even programming logic—through movement.
The boundary between performance and play, machine and muse, is dissolving.
FAQ
What is dancing robot technology?
It’s a field that combines robotics, music analysis, and choreography to create machines capable of moving in real time to live or recorded music.
How do dancing robots detect music?
They use microphones and audio processing software to identify beats, tempo, and musical phrasing. This data informs movement selection.
Can these robots dance with people?
Some prototypes, using vision and motion sensors, are being developed to follow human dancers in real time and perform in sync.
What are the practical uses of dancing robots?
Beyond entertainment, they’re being explored in therapy, education, elderly care, and even social robotics—where movement plays a role in engagement.
Are dancing robots available commercially?
Not yet. Most are university or lab prototypes. However, with falling hardware costs and growing interest, consumer versions may emerge soon.





